Grass: Thesis &Valuation
by Mark Leontev
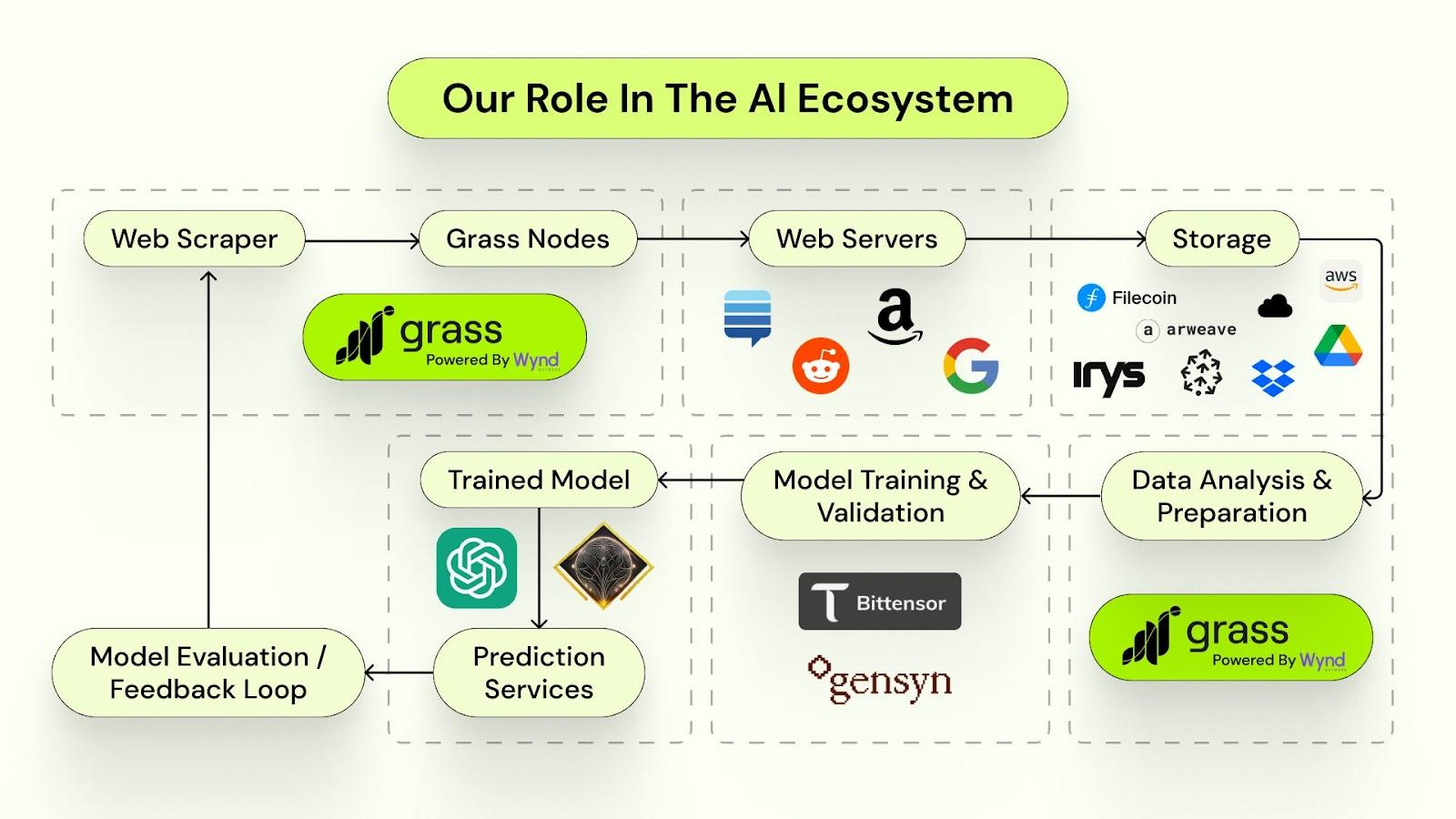
Grass is a DePIN network for data scraping, built on Solana. That’s the elevator pitch - simple, accurate, and undersells everything that’s interesting about it.
As AI models scale further, real-time data is emerging as the upcoming bottleneck alongside computing power. Grass, like all well-designed DePINs, approaches this constraint with incentives: bootstrapping a global, bottom-up (grassroots) data collection network. The premise is that organic participation - if harnessed correctly and channeled in a timely manner toward a valuable use case in an addressable market - scales faster than any centralised competitor operated by a single entity.
Users contribute their unused internet bandwidth to Grass network for scraping and analysing data, which is sold to the companies who demand it. In exchange, the contributors are rewarded with GRASS tokens for participation. Participation leads to creation of a user-owned “map of the internet” that anyone can tap into.
The next phase of growth in AI will see reasoning and logic capabilities increasingly commoditised. While earlier iterations of LLMs were primarily focused on processing and reasoning over historical data, we are now entering an era where the ability to access and process fresh, up-to-the-minute data will become the defining competitive edge for AI systems.
This creates a new competitive landscape where the models with richest live data pipes will gain a critical edge. Gemini’s recent leap shows what happens when a model taps into a knowledge graph as vast as that of Googlebot. Grass aims to offer that same advantage - but bias-proof and composable - to every model on earth.
The knowledge graph, traditionally seen as a static, pre-built database, is evolving into a dynamic, real-time resource that continuously refreshes and updates to reflect the world’s newest information. In the AI-powered economy, such data access is positioned to be the strongest moat.
By leveraging its global coverage, Grass ensures that real-time data can be collected and verified on-demand, making it a highly attractive infrastructure for AI models that require continuous updates to maintain relevance and accuracy.
DePIN approach gives the structural cost arbitrage to provide that. It incentivizes web scraping across a global network of participants to enable AI models to access fresh, unbiased datasets without relying on a centralised knowledge graph, just like Hivemapper does with map data.
Grass benefits from network effects that compound exponentially up to the point where it is already capable of scraping the entirety of Reddit 2024 data in less than one week, tapping into the pool of 2m nodes. 20m nodes will allow for re-training GPT3.5-like model from scratch on a weekly basis. 100m nodes will allow for building a maintainable knowledge graph of the entire Internet.
Further adoption positions Grass as a valuable proposition for the next generation of LLMs and AI-powered applications as they will benefit more from live context than competitors without global knowledge graphs underneath.
Over the next few years, Grass may transition from a fast-growing early-stage scraping tool into a revenue-generating network feeding apps real-time data. With the increasing demand from AI systems for live, high-quality information, and assuming continued network adoption, it is plausible that Grass could generate protocol-level revenues approaching ~$100M. This projection reflects broader trends in the AI and data infrastructure markets, where real-time context is becoming a critical input.
As AI models scale further, real-time data is emerging as the upcoming bottleneck alongside computing power. Grass, like all well-designed DePINs, approaches this constraint with incentives: bootstrapping a global, bottom-up (grassroots) data collection network. The premise is that organic participation - if harnessed correctly and channeled in a timely manner toward a valuable use case in an addressable market - scales faster than any centralised competitor operated by a single entity.
Users contribute their unused internet bandwidth to Grass network for scraping and analysing data, which is sold to the companies who demand it. In exchange, the contributors are rewarded with GRASS tokens for participation. Participation leads to creation of a user-owned “map of the internet” that anyone can tap into.
The next phase of growth in AI will see reasoning and logic capabilities increasingly commoditised. While earlier iterations of LLMs were primarily focused on processing and reasoning over historical data, we are now entering an era where the ability to access and process fresh, up-to-the-minute data will become the defining competitive edge for AI systems.
This creates a new competitive landscape where the models with richest live data pipes will gain a critical edge. Gemini’s recent leap shows what happens when a model taps into a knowledge graph as vast as that of Googlebot. Grass aims to offer that same advantage - but bias-proof and composable - to every model on earth.
The knowledge graph, traditionally seen as a static, pre-built database, is evolving into a dynamic, real-time resource that continuously refreshes and updates to reflect the world’s newest information. In the AI-powered economy, such data access is positioned to be the strongest moat.
By leveraging its global coverage, Grass ensures that real-time data can be collected and verified on-demand, making it a highly attractive infrastructure for AI models that require continuous updates to maintain relevance and accuracy.
DePIN approach gives the structural cost arbitrage to provide that. It incentivizes web scraping across a global network of participants to enable AI models to access fresh, unbiased datasets without relying on a centralised knowledge graph, just like Hivemapper does with map data.
Grass benefits from network effects that compound exponentially up to the point where it is already capable of scraping the entirety of Reddit 2024 data in less than one week, tapping into the pool of 2m nodes. 20m nodes will allow for re-training GPT3.5-like model from scratch on a weekly basis. 100m nodes will allow for building a maintainable knowledge graph of the entire Internet.
Further adoption positions Grass as a valuable proposition for the next generation of LLMs and AI-powered applications as they will benefit more from live context than competitors without global knowledge graphs underneath.
Over the next few years, Grass may transition from a fast-growing early-stage scraping tool into a revenue-generating network feeding apps real-time data. With the increasing demand from AI systems for live, high-quality information, and assuming continued network adoption, it is plausible that Grass could generate protocol-level revenues approaching ~$100M. This projection reflects broader trends in the AI and data infrastructure markets, where real-time context is becoming a critical input.